You need a seamless lighting system for your building, but integration is a nightmare. Mismatched parts and complex tech cause headaches. This post will show you how to simplify it.
Smart COB LED downlights integrate with Building Control Systems (BCS) through shared communication protocols like DALI-2, KNX, or wireless standards like Zigbee. The downlight's smart driver acts as a translator, receiving commands from the central system to control dimming, color, and scheduling.
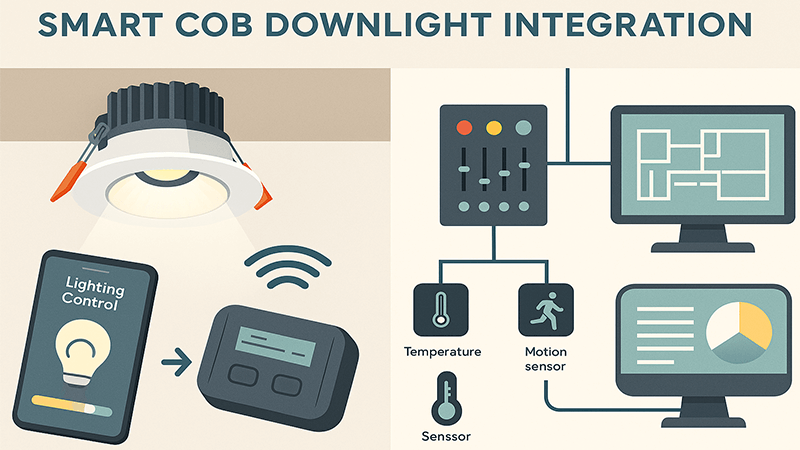
Making smart lights and building systems work together sounds technical and difficult. Many of my clients, like you, worry about getting locked into one brand or choosing the wrong technology. But it's simpler than you think when you understand the basic parts. I've spent my career making these systems work, and I want to break it down for you. Let’s look at how these pieces fit together to create a truly intelligent building that saves you time and money.
How do smart downlights work?
You see the word "smart" on every product, but what does it really mean for a commercial downlight? It can be confusing, leaving you unsure if you're getting a gimmick or a powerful tool.
Smart downlights work by having a driver with a built-in computer chip and a communication module. This setup allows the light to receive digital commands from a central system to turn on/off, dim, or even change color, and then report its status back for monitoring.
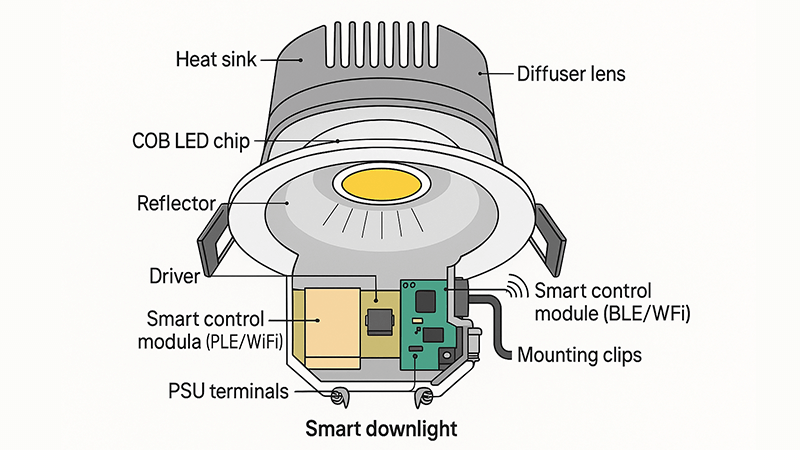
Diving Deeper into the Mechanics
At its core, a smart downlight is not just a light source; it's a data point in your building's network. It has three critical parts that work together: the light engine (often a COB LED for quality), the driver (the brains), and the communication module (the mouth and ears). When you press a button on a wall panel or an app, a signal is sent through your building's network. This signal isn't a simple electrical "on" or "off." It's a digital command, like an email.
The communication module1 in the downlight receives this command. It could be speaking a wired language like DALI or a wireless one like Zigbee2. It passes the message to the smart driver3. The driver then interprets the command—"dim to 50%," for example—and adjusts the electrical current flowing to the COB LED4 chip with perfect precision. It can also send a message back to the central system confirming, "I am now at 50% brightness and using X amount of energy." This two-way communication is what makes a lighting system truly smart and allows for advanced energy management5 and maintenance alerts6.
| Smart Downlight Component | Primary Function | Why It's Crucial for Integration |
|---|---|---|
| COB LED Chip | To produce high-quality, efficient, and uniform light. | The foundation. A reliable light source ensures the "smart" features are worthwhile. |
| Smart Driver | To interpret digital commands and regulate power. | This is the "brain." Its compatibility with the control protocol is non-negotiable. |
| Communication Module | To send and receive data over the network. | This component determines the "language" the light speaks (DALI, Zigbee, etc.). |
| Sensors (Optional) | To detect occupancy, motion, or ambient light levels. | Provides real-time data to automate commands, maximizing energy savings. |
I remember a project manager in the UAE who sourced beautiful downlights for a new office tower. The problem was the drivers used a proprietary protocol. They couldn't talk to the building's main KNX7 control system. It became a huge, expensive problem to fix after installation. This is why we always start the conversation by asking about the building's control system first. The light fixture is important, but the driver's ability to communicate is what makes a project successful.
Where might LED lights be used in a building?
You know that LED lights8 are the standard for new buildings and renovations. But just swapping old bulbs for new ones is not enough. You might be missing chances to improve productivity and save a lot more money.
LED lights, especially versatile COB downlights, are used throughout modern buildings. They provide focused task lighting in offices, create welcoming atmospheres in lobbies, ensure safety in corridors and stairwells, and highlight products effectively in retail spaces9. Their adaptability makes them essential for any area.
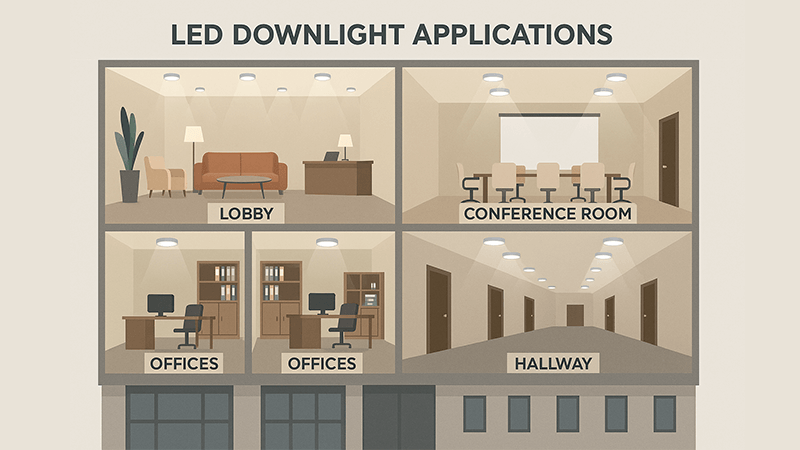
Diving Deeper into Strategic Placement
Thinking about where to place lights goes beyond just filling a space with brightness. It’s about matching the light to the function of the space. Different areas in a building have very different needs, and using a one-size-fits-all approach is a missed opportunity. Smart LED lighting allows you to create customized environments that can adapt throughout the day.
Applications in Commercial Spaces
In an office, the goal is productivity and employee well-being. Here, COB LED downlights are perfect for task lighting10 over desks, providing clear, focused light that reduces eye strain. In meeting rooms, the same lights can be dimmed for presentations or brightened for brainstorming sessions. This is a core part of what we call human-centric lighting11, where the light changes to support our natural body rhythms.
Public and Transitional Areas
Now, think about the public spaces. In a hotel lobby or a corporate reception area, lighting creates the first impression. Here, you can use downlights for general ambient light12 and adjustable accent lights to highlight artwork or architectural features. In hallways and stairwells, the priority is safety and energy efficiency13. Smart downlights connected to motion sensors ensure these areas are always safely lit when someone is present but dim down to save energy when they are empty. I've seen clients reduce their energy consumption in these common areas by over 80% just by adding simple sensor integration.
| Building Area | Primary Lighting Goal | Recommended Smart LED Solution | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Office Workstations | Enhance focus, reduce glare | Tunable white COB downlights | Improves employee comfort and productivity. |
| Lobbies & Receptions | Create a welcoming atmosphere | High CRI COB downlights with accent and wall-washing options | Strengthens brand image and guest experience. |
| Hallways & Stairs | Ensure safety, save energy | COB downlights integrated with occupancy/motion sensors | Drastically cuts electricity waste. |
| Retail Spaces | Make products look appealing | High CRI, adjustable COB downlights for highlighting merchandise | Drives sales by making products more attractive. |
The flexibility of smart LEDs means you are no longer limited to a static lighting plan. You can design a living system that responds to the people in the building, making it more comfortable, efficient, and valuable.
How are smart lights controlled?
You want to offer your clients advanced lighting, but the control systems seem complicated. You worry about confusing switches and apps that never work right. This complexity can make you hesitant to propose a smart system.
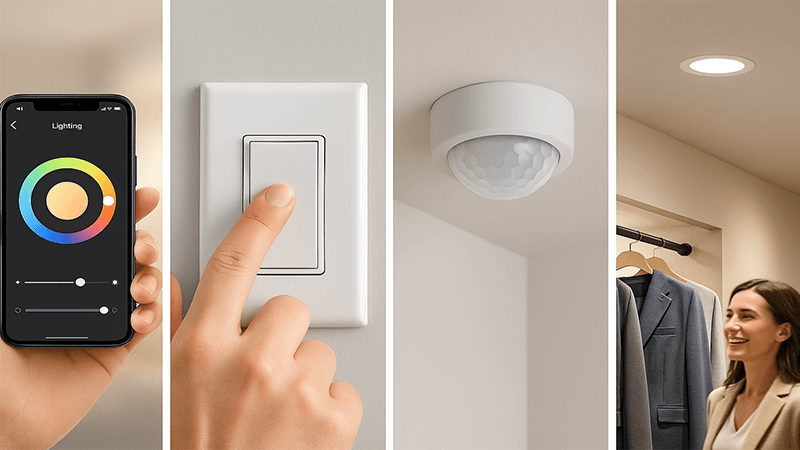
Smart lights are controlled through various interfaces that send signals to a central gateway or directly to the lights. These include wall-mounted smart switches, mobile apps, desktop software for facility managers, and automated controls from sensors for occupancy or daylight harvesting14.

Diving Deeper into Control Systems
Controlling a smart lighting system isn't about having one magic button. It’s about having the right tool for the right user. The beauty of a well-designed system is that it offers multiple layers of control, from simple and intuitive for the everyday user to complex and powerful for the building manager.
The User-Facing Controls
For people working in the office or staying in a hotel room, the control needs to be simple. This usually means a smart wall switch or a simple keypad. These look familiar but are much more powerful than a simple on/off switch. One button could activate a pre-programmed "scene," like a "Presentation Mode" that dims the main lights and turns on accent lighting. For more tech-savvy users, a mobile app can offer personal control over the lights in their immediate area, allowing them to adjust brightness and color temperature to their preference. This level of personal control is a huge factor in employee satisfaction.
The Facility Management Controls
Behind the scenes, the facility or building manager needs a much more powerful interface. This is typically a software program running on a computer. From this central dashboard, they can see the entire building's lighting system at a glance. They can set schedules, for example, ensuring all lights automatically turn off at 8 PM. They can monitor energy consumption in real-time and identify areas of waste. They also receive maintenance alerts6, like when a driver is failing, so they can fix it before anyone even notices a light is out. This centralized management is what unlocks the biggest savings in energy and operational costs. The key here, as I mentioned in my insight, is a unified protocol. When everything speaks the same language, like DALI-215, all these different control layers work together perfectly.
What is a LED CoB downlight?
You see many acronyms in the lighting industry: SMD, MCOB, and COB. It's hard to know which is best for your project. Choosing the wrong type can lead to poor light quality and unhappy clients.
A COB (Chip-on-Board) LED downlight is a type of fixture where multiple LED chips are packaged together as one single module. This design creates a powerful, single point of light that looks like a traditional halogen lamp but is much more efficient and controllable.
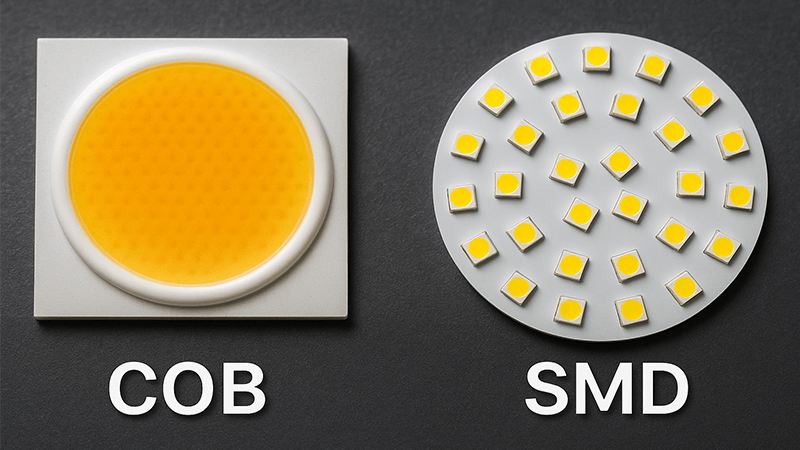
Diving Deeper into COB Technology
To really understand why so many professional lighting projects use COB downlights, it helps to compare them to the older technology, SMD (Surface Mounted Device) LEDs. SMD lights use many individual, small LED chips spread out over a circuit board. You can often see the separate dots of light. While great for some applications like strip lighting, it can create a scattered light with multiple shadows, which isn't ideal for focused lighting.
The Advantages of a Single Light Source
COB technology solves this problem. By mounting the LED chips densely on a single substrate, it creates one uniform, intense beam of light. This is much better for directing light exactly where you need it, which is why it's perfect for downlights, spotlights, and track lights. Because the light comes from a single point, it creates clean, crisp shadows and allows for excellent control with lenses and reflectors. This gives lighting designers the ability to shape the light with precision, whether they are highlighting a piece of art in a gallery or providing focused task lighting on a desk. From my experience in manufacturing, the thermal management is also superior. The COB chip's direct contact with a heat sink allows it to run cooler, which leads to a longer lifespan and more consistent color over time—two things every purchasing manager wants to guarantee.
| Feature | COB (Chip-on-Board) LED | SMD (Surface Mounted Device) LED | Why It Matters for Downlights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light Source | Single, uniform point of light. | Multiple, separate points of light. | COB provides a cleaner, more traditional light beam. |
| Light Quality | High intensity, no multiple shadows. | Can create multiple shadows and a "dotted" look. | Better for accent and task lighting. |
| Efficiency (lm/W) | Very high, due to better thermal management. | Good, but can be less efficient at higher power levels. | More light for less energy means lower running costs. |
| Heat Dissipation | Excellent. Chips are mounted directly to a heat sink. | Good, but heat must travel through more layers. | Better heat management means a longer, more reliable life. |
For any project where light quality and control are important, COB is almost always the superior choice for downlights. It's the technology that allows us to deliver on our promise of "Lighting Quality You Can See."
Conclusion
Integrating smart COB downlights becomes simple when you focus on a unified protocol like DALI-2. This ensures all parts speak the same language, creating a reliable and efficient system.
Explore the importance of communication modules in smart lighting systems. ↩
Understand how Zigbee enables wireless communication in smart lighting. ↩
Learn about the role of smart drivers in controlling lighting efficiently. ↩
Discover why COB LED technology is preferred for high-quality lighting. ↩
Explore strategies for effective energy management in modern buildings. ↩
Learn how maintenance alerts can prevent issues and save costs. ↩
Find out how KNX protocol facilitates seamless building automation. ↩
Explore the advantages of LED lights for energy savings and longevity. ↩
Discover how effective lighting can boost sales and customer experience. ↩
Learn about the significance of task lighting in enhancing productivity. ↩
Learn how human-centric lighting improves well-being and productivity. ↩
Discover how ambient light creates atmosphere and comfort in environments. ↩
Explore effective strategies to improve energy efficiency in your building. ↩
Understand how daylight harvesting can reduce energy costs in buildings. ↩
Discover how DALI-2 enhances communication in smart lighting systems. ↩

