Struggling with flickering or failing COB downlights? The wrong driver technology1 causes inconsistent performance and shortens lifespan. You need a stable, compatible power source for reliable, high-quality lighting.
For COB LED downlights, Constant Current (CC) drivers are the best technology. They maintain a steady electrical current, ensuring consistent brightness, optimal performance, and longer lifespan for the LEDs. Matching the driver's output current (mA) and voltage range (V) to the COB's specifications is crucial.
Choosing the right driver for a COB downlight can feel complicated. I've seen many projects go wrong because of a simple mismatch between the light and its power source. It's not just about getting the lights to turn on; it's about ensuring they perform perfectly for years. Let's break down what you need to know to select the right driver every time, so you can deliver the lighting quality2 your clients expect. Keep reading to make sure you get it right.
Do COB LEDs need drivers?
Your COB LEDs keep burning out, causing project delays and costly replacements. You suspect the power supply3, but aren't sure why. Without the right component, your lights are at risk.
Yes, COB LEDs absolutely need a driver. A driver acts like a brain, converting high-voltage AC power4 from your wall outlet into the low-voltage DC power5 that LEDs require. It regulates the current and voltage to protect the sensitive COB chip from damage and ensure stable operation.
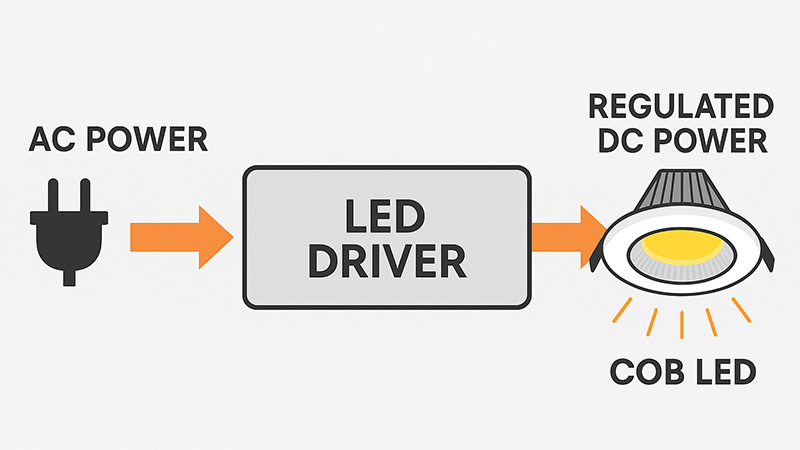
Back when I started in the factory, I saw a new COB chip connected directly to a power source without a proper driver. It lit up incredibly bright for a second and then poof—a tiny puff of smoke and it was gone. That was an expensive lesson. A driver isn't just an accessory; it's an essential guard for the LED. COB LEDs are designed to work with a specific, stable electrical current. The power from our standard electrical outlets is alternating current (AC) and is much too high and unstable for a delicate COB chip. The driver's main job is to fix this. It takes that powerful AC and converts it into a smooth, steady stream of low-voltage direct current (DC). This protects the LED from power surges and fluctuations that would otherwise destroy it. Think of it as a translator between the power grid and your light. Without this translation, the LED gets overwhelmed and fails. For someone like Shaz, a purchasing manager, understanding this is key. Specifying a luminaire without the correct driver is like buying a high-performance car engine without a transmission—it simply won't work correctly.
What driver do I need for LED lights?
You're sourcing for a big project, but the variety of LED drivers is confusing. Choosing the wrong type could lead to poor performance or even system failure. You need clarity.
You need a driver that matches your LED's specific requirements. For COB LEDs, this is almost always a Constant Current (CC) driver. You must match the driver's output current (in milliamps or amps) and forward voltage range6 with the specifications7 of your COB LED.
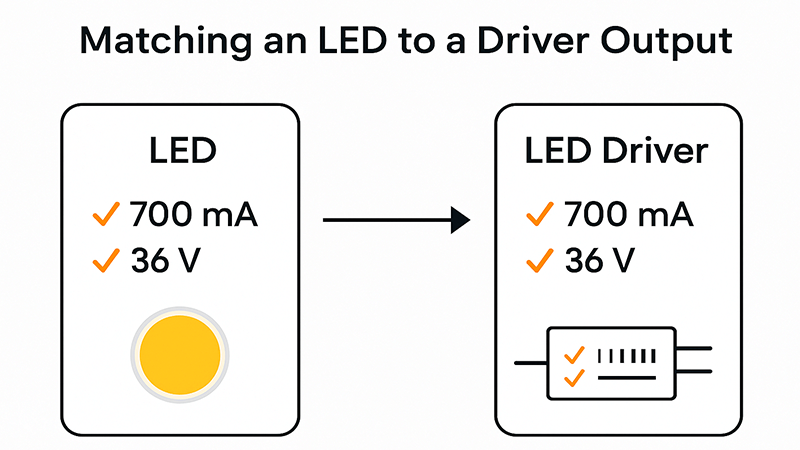
When sourcing for any LED product, the driver question is always top of the list. It's not a one-size-fits-all situation. The needs of an LED strip light are very different from the needs of a high-power COB downlight. For most single LEDs and series-wired LEDs, like COB chips, you must use a Constant Current (CC) driver. It delivers a fixed electrical current (e.g., 350mA, 700mA) and the voltage adjusts as needed. This is perfect for COBs because they are very sensitive to current changes; even a small increase can drastically shorten their life. In contrast, LED strips8 are often wired in parallel and require a Constant Voltage (CV) driver, which supplies a fixed voltage (e.g., 12V or 24V). For a purchasing manager reviewing technical sheets, the key is to look for these two main categories:
Driver Types Breakdown
| Driver Type | Best For | How it Works | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Constant Current (CC) | Single high-power LEDs, COBs, series circuits9 | Provides a fixed output current10 (mA) and a variable voltage. | COB downlights, track lights, spotlights. |
| Constant Voltage (CV) | LEDs in parallel circuits11, LED strips | Provides a fixed output voltage (V, e.g., 12V/24V) and a variable current. | LED tape/strip lighting, rope lights. |
For COB downlights, you will almost exclusively be looking for CC drivers. Your job is to find the driver that not only matches the required current but also has a voltage range that covers the COB's forward voltage. Getting this wrong means the light either won't turn on or will fail quickly.
How to choose the correct LED driver?
Choosing a driver feels like a gamble. Mismatched specs lead to flickering, poor dimming, or premature failure, damaging your reputation. You need a reliable method to select the right one every time.
To choose the correct driver, first identify if you need Constant Current (CC) or Constant Voltage (CV). Then, match the driver's output wattage, voltage, and current to the LED's requirements. Finally, consider physical size, dimming protocol12, and environmental rating (IP)13.
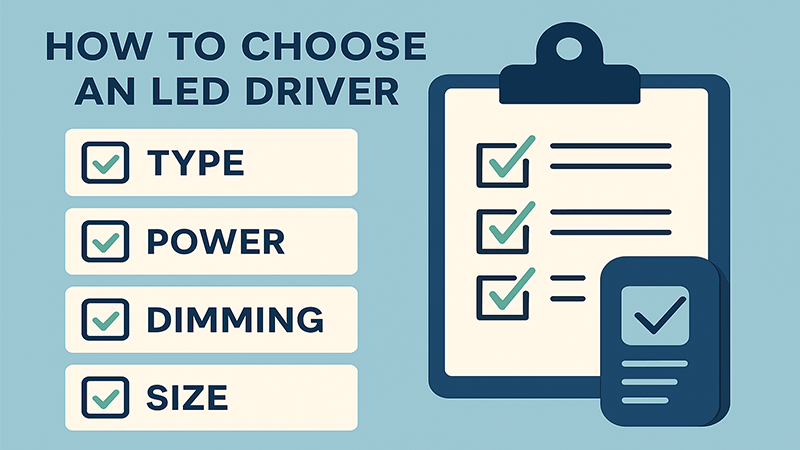
Selecting the right LED driver is a systematic process, not guesswork. As a manufacturer, I live by these details because they determine the quality of the final product. For a professional like Shaz, having a clear checklist ensures you source a compatible and reliable component that meets project specifications7. Let's walk through it. First, as we've discussed, COB downlights need a Constant Current (CC) driver. This is non-negotiable for performance. Next, check the technical specifications of the COB chip itself. It will specify a drive current (e.g., 700mA) and a forward voltage range6 (e.g., 32-36V). The driver you select must match that current exactly and have an output voltage range that includes the COB's range. Then, you calculate the wattage14. Multiply the current (in Amps) by the voltage (in Volts) to get the power (in Watts). Always choose a driver with a maximum wattage slightly higher than the LED's requirement to avoid running it at full capacity, which can shorten its life. A crucial point, especially for projects with many downlights, is consistency. From my experience, if you're using multiple COB modules, the current difference between each module must be less than or equal to ±3%. If it's more, you'll see a noticeable difference in brightness from one light to the next. This is a quality detail that sets a professional installation apart.
Key Selection Criteria
- Driver Type: For COBs, always select a Constant Current (CC) driver.
- Output Current (mA): Must match the specified drive current of the COB LED.
- Output Voltage Range (V): The driver's voltage range must encompass the LED's forward voltage.
- Wattage (W): Should be at least 20% higher than the LED's power consumption for longevity.
- Dimming: If dimming is required, ensure the driver is compatible with the control system (e.g., Triac, 0-10V, DALI).
- Physical Size: The driver must physically fit within the luminaire housing or designated installation space.
Which is better, a CV or CC LED driver?
Confused about whether to specify a Constant Voltage (CV) or Constant Current (CC) driver? This decision impacts everything from light output to system longevity. Making the wrong choice can be costly.
A Constant Current (CC) driver is better for COB LEDs and single high-power LEDs. A Constant Voltage (CV) driver is better for LED strips and modules wired in parallel. For COB downlights, CC is the superior and correct choice for stability and long life.
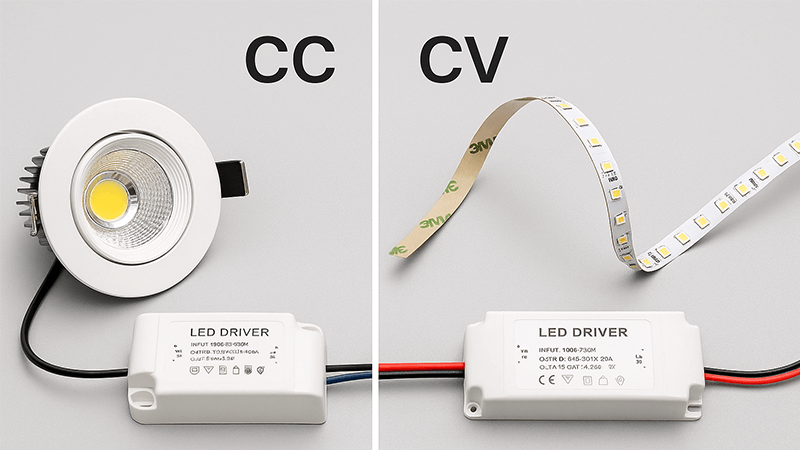
This is one of the most fundamental questions in LED technology, and the answer depends entirely on the type of LED you are powering. Constant Current (CC) and Constant Voltage (CV) drivers work differently and are not interchangeable. A CC driver is designed to deliver a consistent, unchanging current (measured in amps or milliamps) to the LED. The driver will vary the voltage as needed to maintain that current. This is ideal for high-power LEDs15 like COBs. Why? As an LED heats up during operation, its electrical resistance decreases, causing it to draw more current. A CC driver prevents this "thermal runaway16" by keeping the current locked, ensuring stable brightness and protecting the LED from self-destructing. A Constant Voltage (CV) driver, on the other hand, provides a fixed, unchanging voltage (like 12V or 24V). This is suitable for LED strips where multiple small LEDs are wired in parallel, and resistors are already built into the strip to limit current to each LED. Using a CV driver on a COB chip without a current-limiting resistor is a recipe for disaster. The COB would draw more and more current as it heats up until it burns out.
CC vs. CV Driver Comparison
| Feature | Constant Current (CC) Driver | Constant Voltage (CV) Driver |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Maintains a fixed output current (mA/A). | Maintains a fixed output voltage (V). |
| Best Application | COB LEDs, single high-power LEDs, series circuits. | LED strips, parallel circuits, modules with on-board current regulation. |
| Benefit for COBs | Prevents thermal runaway, ensures consistent brightness and longevity. | Not recommended for direct connection to COBs. |
| Analogy | Cruise control for your car's speed. | A fixed-pressure water line. |
For a purchasing manager like Shaz, the rule is simple: if the product is a COB downlight, spotlight, or track light, the specification must call for a Constant Current driver. It's the only way to guarantee the quality and reliability that your projects demand.
Conclusion
For COB downlights, use a Constant Current driver. Match the current, voltage, and power specifications to your LED, and you will ensure consistent brightness and a long, reliable lifespan.
Learn how driver technology impacts the performance and lifespan of LED lights. ↩
Learn tips for maintaining high lighting quality in your LED projects. ↩
Discover the role of power supply in maintaining LED performance and reliability. ↩
Learn about the conversion of AC power to DC for safe LED operation. ↩
Explore the significance of low-voltage DC power in protecting LED components. ↩
Understanding forward voltage range helps in selecting compatible LED drivers. ↩
Understanding specifications is vital for selecting the right components for your projects. ↩
Understanding the differences helps in choosing the right driver for your lighting needs. ↩
Learn about series circuits to better understand driver requirements for LEDs. ↩
Finding the right output current is crucial for matching drivers to COB LEDs. ↩
Understanding parallel circuits is crucial for selecting the right driver type. ↩
Learn about dimming protocols to enhance the functionality of your LED systems. ↩
Explore how environmental ratings affect the durability and application of LED drivers. ↩
Calculating wattage is essential for selecting the right driver for your LEDs. ↩
Explore the applications of high-power LEDs and the importance of proper drivers. ↩
Understanding thermal runaway is key to ensuring LED longevity and performance. ↩

